Microsoft Authentication Model
This authentication model implements the new Azure-based verification process and is applicable to all MineCraft versions currently under maintenance.
Preparation
Because the new version of the authentication process uses Azure-based authentication. Therefore, before you begin, make sure you have completed Configuration of Azure Apps
After completing the Azure application registration, please make sure to complete Microsoft Authenticator Initialization at the program entry point.
Configure cached credential providing method
Due to the particularity of this verification model, developers need to save the refresh token and expiration time returned by the first verification to help the validator complete the verification. The validator will call this method for the first time during verification to query the validity of the local token cache. If the local token is still valid, the verification result will be returned directly. If the locally cached token has expired, the developer needs to manually request a new token and return the refreshed token.
Here is a sample implementation code of this method:
public async Task<(bool, GraphAuthResultModel?)> CacheTokenProviderAsync()
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(XBLToken)) return (false, default);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(XBLRefreshToken)) return (false, default);
// Calculate expire date
var expireDate = LastRefreshedTime.AddSeconds(ExpiresIn);
// If the local cache token is still valid, the current token is returned directly.
// Otherwise, request a new token using the refresh token
if (expireDate > DateTime.Now)
{
var result = new GraphAuthResultModel
{
ExpiresIn = (int)(expireDate - DateTime.Now).TotalSeconds,
AccessToken = XBLToken,
RefreshToken = XBLRefreshToken
};
return (true, result);
}
// Request a new login token
var refreshReqDic = new List<KeyValuePair<string, string>>
{
new("client_id", MicrosoftAuthenticator.ApiSettings.ClientId),
new("refresh_token", XBLRefreshToken),
new("grant_type", "refresh_token")
};
using var refreshReq = new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Post, MicrosoftAuthenticator.MSRefreshTokenRequestUrl)
{
Content = new FormUrlEncodedContent(refreshReqDic)
};
using var refreshRes = await DefaultClient.SendAsync(refreshReq);
var refreshContent = await refreshRes.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
var refreshModel = MicrosoftAuthenticator.ResolveMSGraphResult(refreshContent,
GraphAuthResultModelContext.Default.GraphAuthResultModel);
if (refreshModel is not GraphAuthResultModel model)
{
if (refreshModel is GraphResponseErrorModel error)
{
// Handle failed refresh operations here
}
return (false, default);
}
return (true, model);
}Configure first login device flow verification code display method
Because we use device flow verification to verify the player's Microsoft account. Therefore, we need an additional method to present the one-time key and verification address required for device flow verification to the user.
Here is an example of this method:
private void DeviceTokenNotifier(DeviceIdResponseModel deviceIdResponseModel)
{
// Display the obtained callback data to the front end
DeviceCodeResponse = deviceIdResponseModel;
}DeviceIdResponseModel contains all the information the user needs to complete verification:
| Name | Function |
|---|---|
| UserCode | The secret key required for user authentication |
| VerificationUri | Verification address, users need to visit this URL to complete subsequent verification steps |
| ExpiresIn | Validation code expiration time (seconds) |
Here you can see an example of the interface:
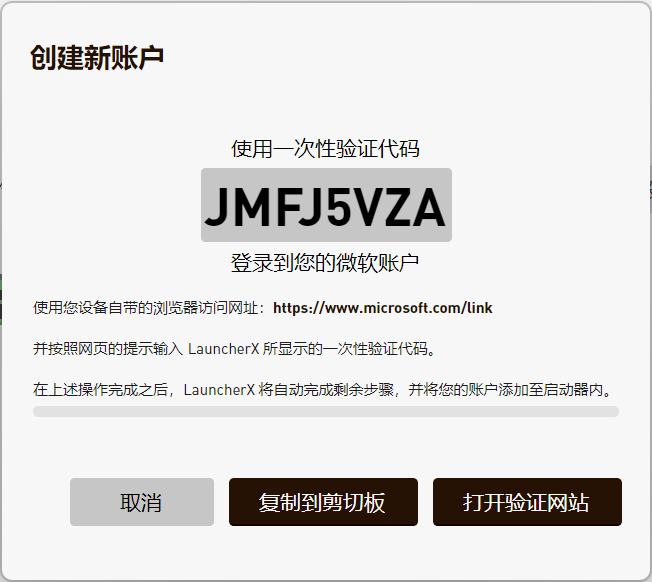
In this interface, you need to include at least the following content:
- The secret key required to log in
- Specific verification address
- A short operation prompt to help users complete the verification operation
Initialize validator
Initial verification
WARNING
Please make sure you are ready before performing the following process Configuring the first login device flow verification code display method to ensure that users can obtain the correct initial login information!
Initialize the validator:
var microsoftAuthenticator = new MicrosoftAuthenticator
{
LauncherAccountParser = launcherAccountParser
};In the above code block, please replace these parameters according to your actual situation:
| Project | Description |
|---|---|
| launcherAccountParser | For initialization of the launcher account parser, see here |
Not initial verification
Non-initial verification means using the Token cache obtained in the first verification for secondary verification. It mainly uses CacheTokenProviderAsync to verify whether the local credentials are still valid. If the locally cached Token has expired, it will be refreshed in this method.
Initialize the validator:
var microsoftAuthenticator = new MicrosoftAuthenticator
{
CacheTokenProvider = CacheTokenProviderAsync,
Email = "[EMAIL]",
LauncherAccountParser = launcherAccountParser
};In the above code block, please replace these parameters according to your actual situation:
| Project | Description |
|---|---|
| launcherAccountParser | For initialization of the launcher account parser, see here |
| [EMAIL] | Email address to verify account |
TIP
For the initialization of launcherAccountParser (game profile parser), please refer to the Game Profile Parser page
Get authentication results (first authentication)
After you complete the initialization of the authentication model, you only need to call the Microsoft Authenticator's authentication method for initial account authentication.
Here is a sample authentication code:
// Get authentication results
// DeviceTokenNotifier: This is the information display method mentioned above.
var authResult = await msAuth.GetMSAuthResult(DeviceTokenNotifier);
if (authResult == null)
{
// Handling failed authentication
}
// Parse user fields from Jwt Token
var claims = JwtTokenHelper.GetTokenInfo(authResult.IdToken);
var email = claims.TryGetValue("email", out var outEmail) ? outEmail : null;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(email))
{
// Unable to resolve user's email address from Jwt credentials, treated as authentication failure
// This is most likely caused by Azure application or Scope configuration failure.
}
// Save necessary user information to local disk in preparation for next authentication
var msInfoModel = new MSAccountInfoModel
{
XBLToken = authResult.AccessToken,
XBLRefreshToken = authResult.RefreshToken,
ExpiresIn = authResult.ExpiresIn,
Email = email
};Get Authentication results (not initial authentication)
After you complete the initialization of the authentication model, you only need to call the authentication method of Microsoft Authenticator to complete the account authentication.
In an asynchronous context, use AuthTaskAsync to accomplish authentication:
var authResult = await microsoftAuthenticator.AuthTaskAsync(false);In a sync context, use Auth to finish authentication:
var authResult = microsoftAuthenticator.Auth();Interpret authentication results
After the authentication method is completed, the authentication model will return the authentication result, which is of the parent type AuthResultBase object. All authentication results contain an enumeration value AuthStatus, which directly indicates the success or failure of the authentication result. Below you can see an interpretation of the authentication results:
Failed Authentication Result
By judging whether Error is empty, you can easily judge whether the authentication results returned by the authentication model are valid. The Error object will contain the following fields to tell you some details:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| authResult.Error.Cause | The specific cause of the problem |
| authResult.Error.Error | error name |
| authResult.Error.ErrorMessage | Details of the error, possibly including a solution |
Successful authentication result
If the Error field in the authentication result is empty, it means that the authentication is valid. A successful authentication result will contain the following information:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| authResult.Id | A unique identifier for the username. ProjBobcat uses a specific generation method to generate this identifier. |
| authResult.AccessToken | Authorization credentials for the user account |
| authResult.Profiles | List of roles available to the user, which may contain multiple available roles |
| authResult.SelectedProfile | The role currently selected by the user. This field may be empty. If it is empty, the user needs to be prompted for manual selection. |
| authResult.User | Summary of user account information, including some basic account information |
| authResult.LocalId | Local ID, usually a randomly generated UUID |
| authResult.RemoteId | The remote ID returned by the authentication server, usually a unique identifier for the user |
| authResult.XBoxUid | XBox Live UID |
| authResult.Email | Verify email address used |
| authResult.CurrentAuthTime | The current verification time, Developers need to save this field to help confirm the validity of the local cache token |
| authResult.ExpiresIn | Token expiration time (unit: seconds), Developers need to save this field to help confirm the validity of the local cache token |
| authResult.RefreshToken | Refresh token, Developers need to save this field to help refresh expired tokens |
| authResult.Skin | Skin URL for user account |
WARNING
Please use corresponding restrictions or encryption operations to safely store confidential data related to user tokens. The leakage of this data may cause losses.